Search Methods¶
Determined supports a variety of hyperparameter search algorithms.
Aside from the single searcher, a searcher runs multiple trials and decides the hyperparameter
values to use in each trial. Every searcher is configured with the name of the validation metric to
optimize (via the metric field), in addition to other searcher-specific options. For example,
the adaptive_asha searcher (arXiv:1810.0593), suitable
for larger experiments with many trials, is configured with the maximum number of trials to run, the
maximum training length allowed per trial, and the maximum number of trials that can be worked on
simultaneously:
searcher:
name: "adaptive_asha"
metric: "validation_loss"
max_trials: 16
max_length:
epochs: 1
max_concurrent_trials: 8
For details on the supported searchers and their respective configuration options, refer to Hyperparameter Tuning.
That’s it! After submitting an experiment, users can easily see the best validation metric observed across all trials over time in the WebUI. After the experiment has completed, they can view the hyperparameter values for the best-performing trials and then export the associated model checkpoints for downstream serving.
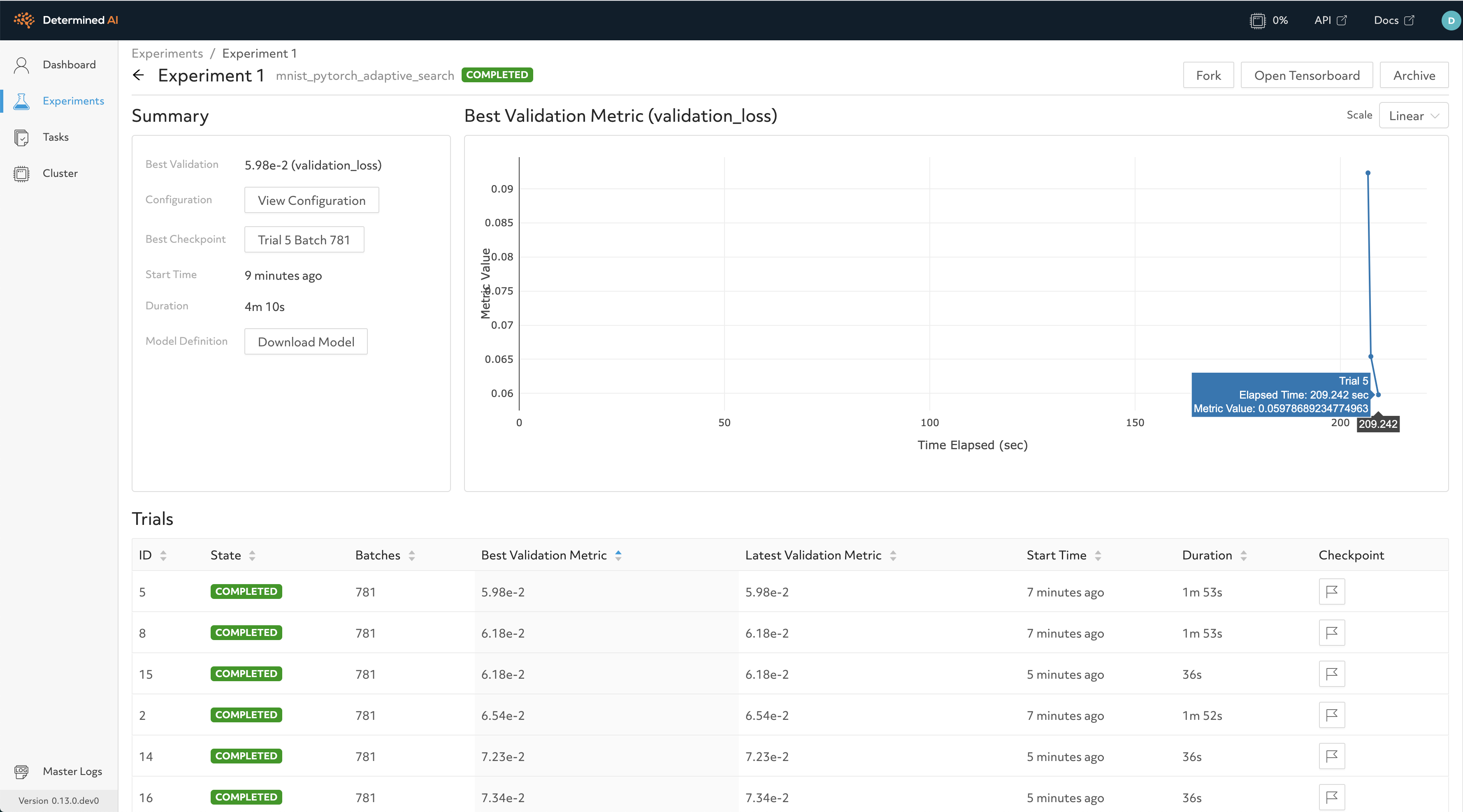
Adaptive Search¶
Our default recommended search method is Adaptive (ASHA), a state-of-the-art early-stopping based technique that speeds up traditional techniques like random search by periodically abandoning low-performing hyperparameter configurations in a principled fashion.
Adaptive (ASHA) offers asynchronous search functionality more suitable for large-scale HP search experiments in the distributed setting.
Other Supported Search Methods¶
Determined also supports other common hyperparameter search algorithms:
Single is appropriate for manual hyperparameter tuning, as it trains a single hyperparameter configuration.
Grid evaluates all possible hyperparameter configurations by brute force and returns the best.
Random evaluates a set of hyperparameter configurations chosen at random and returns the best.
You can also implement your own custom search methods.